Types of human worms
- Annelida - pinworms, roundworms, whipworms, trichinella spiralis;
- Tapeworms – various types of tapeworms, echinococci, tapeworms;
- Flatworms – various flukes and trematodes.
- Roundworms are large roundworms that are reddish-yellow in color and can reach up to 40 centimeters in length when adults.
- Whipworms are round worms 30-50 mm long, named for their body shape: long and narrow at the front, like a hair, and short and wide at the back.
- The broad tapeworm is a large tapeworm with a body length of about 10 meters, and an individual can reach more than 20 meters.
- Ancylostoma is a collective name for two types of worms: Ancylostoma duodenale and Ancylostoma ancylostoma , a roundworm that is 10-15 mm long.
- Trichinella spiralis is a small 2-5 mm long roundworm that causes a serious disease - trichinellosis.
- The liver fluke (cat fluke) is a species of flatworm in the class Fluke, 7-20 mm long. The disease caused by this parasite is called opiodriasis.
- The structures of pork and cattle tapeworms are similar, and tapeworms can be up to 6 meters long.
- The Echinococcus tapeworm parasitizes the human body not in its adult form, but in an intermediate form - Homo finnensis. Echinococcus itself is a tapeworm 3-5 mm long
- Aspergiococcus is a worm similar to Echinococcus and has similar structure and developmental mechanisms.
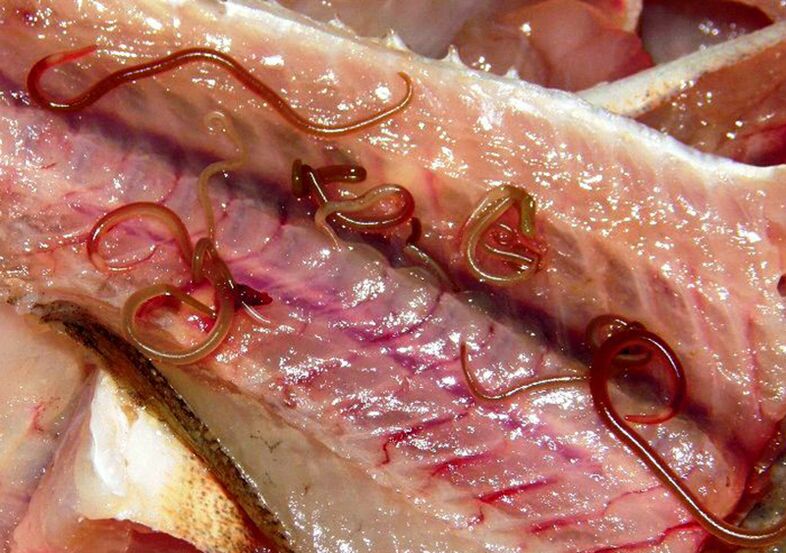
parasites in human body
How did you get infected?
- Eat unclean vegetables;
- Failure to observe hygiene rules when preparing food;
- Poor heat treatment of certain foods, especially animal meat and fish;
- Communicating with pets – cats, dogs, certain types of rodents;
- Failure to comply with hygiene regulations before eating, after going to the toilet, and after returning from a walk;
- Swimming in polluted water.
General signs and symptoms of helminth infection in children
- Worsened or increased appetite;
- Nausea, possibly vomiting;
- Excessive salivation;
- Disturbed bowel movements;
- Pain in the lower abdomen;
- dizziness, headache;
- allergic reactions;
- Increased frequency of colds;
- Irritability, moodiness;
- sleep disorder;
- worsening of mental and physical activity;
- dry cough.
Symptoms of human worms
- Gastrointestinal dysfunction - diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain;
- Joint and muscle pain - Parasites can move throughout the body to settle in the best places for them to live, such as in joint fluid and muscles. When this happens, the person experiences painful feelings;
- Neurological disorders and general malaise—manifested by fatigue, irritability, sleep disturbances, and memory problems;
- Allergic reactions and skin manifestations—the appearance of papules, blackheads, and other rashes—are also signs of the presence of helminths in humans;
- Decreased immunity, leading to the occurrence of infectious diseases;
- Drastic weight loss;
- Anemia - Some worms suck blood from the intestinal wall like leeches;
- Teeth grinding during sleep and sleep disorders;
- Itching in the anus, especially at night. The female is actively laying eggs at this time, causing anal itching;
- Swollen lymph nodes and low body temperature;
- Inflammation of the respiratory tract - cough, fever, sputum production, runny nose - is a sign of the presence of worms.
Symptoms of worm infection may appear at different times after infection with worms. Therefore, the first symptoms of ascariasis appear after 2-3 days. As with most other helminth infections, symptoms of illness appear after 2-3 weeks.
What organs do worms affect?
- Borers inhabit the small and large intestines. In particular, the first part of the small intestine is affected by tapeworms, hookworms, and roundworms. The lower part of the small intestine is home to dwarf tapeworms and pinworms. The large intestine is most commonly home to whipworms.
- Tissue worms affect any type of organ: liver, brain, lymph nodes, bile ducts.
important! In the initial stages of the development of the infection, it is impossible to determine the signs of the presence of worms in the patient's body. As long as the number of worms is small and the poison produced by the waste is within normal limits, the body itself can cope with the invasion. The appearance of characteristic or acute symptoms indicates a significant increase in the number of helminth infections: the maturation of individuals and their dynamic development.
Complications of worms
- B12 deficiency anemia, iron deficiency anemia - results in interruption of oxygen supply to tissues, requiring long-term recovery. Symptoms include pale skin, dry mouth, weakness, and disorders of various body functions;
- Intestinal obstruction occurs when the parasite blocks the intestinal lumen with its body. Surgical treatment is required. Symptoms - abdominal pain, insufficient stool, vomiting;
- Intestinal bleeding – If worms attach to the intestinal wall, they can damage its blood vessels. Symptoms: abdominal pain, weakness, bloody stool, vomiting. Need for surgical treatment;
- Liver fibrosis and cirrhosis develop with the long-term course of opiodriasis. These changes are irreversible. Symptoms: Disrupted sleep and wakefulness, fluid accumulation in body cavities, loss of liver function;
- Abscesses in the affected organs are purulent inflammations. Symptoms are pain, high fever, and weakness. The condition is deteriorating rapidly. Examination is needed to identify the source of inflammation and surgical treatment is required.
Fecal analysis and egg scraping
Blood test for worms
- If levels of immunoglobulin class M (IgM) are elevated in the blood, worms can colonize the body.
- Either the worms were previously present in the body, or the worm infection becomes chronic and causes the body's immune system to weaken. This conclusion can be drawn if there are elevated levels of IgG immunoglobulins in the blood, but no IgM is detected.
How do parasites infect and develop?
- Contact helminthiasis;
- soil worm disease;
- Biological helminthiasis.
contact helminthiasis
geohelminths
Biological helminthiasis
Treatment of Human Worms
treat
anthelmintic therapy
- forms of helminthiasis;
- stage of disease development;
- pathogen;
- concomitant diseases in children;
- characteristics of his condition.
Only a doctor can correctly evaluate these indicators and choose the best drug. Self-treatment of helminthiasis in children is not acceptable. Choosing the wrong treatment is often not only ineffective but also associated with serious side effects.
Symptomatic treatment
How to treat worms with folk remedies
- The best folk remedy is to use pumpkin seeds to treat worms. Take pumpkin seeds (80-100 grams) and peel them, trying not to damage the green skin. Grate them, add 2 tablespoons of honey and 100 g of water and mix. This medication must be taken strictly in the morning on an empty stomach. The dining boat departs every hour and lasts for 3 hours. You will then need to take a laxative and 1-2 hours later have an enema.
- Pomegranate. Pomegranate peel contains punicaline, which is highly toxic to worms. Adults and children with parasites should take the bark simmered in fresh water three times a day.
- Onion soup (pour 200 ml of boiling water on 1 onion, leave it for 2 days, drink before meals, for 4 consecutive days)
prevention
- Instill personal hygiene skills in children (washing hands after using the toilet, handling animals, going for walks, and before eating);
- Get rid of bad habits (forbid children to suck their fingers, bite their nails, or put foreign objects in their mouth);
- Control mosquitoes, flies and insects;
- high-quality processing of meat and fish;
- High-quality water disinfection;
- deworming domestic dogs and cats;
- Avoid contact with stray animals;
- Wash vegetables, berries and fruits thoroughly;
- Change underwear and sheets frequently (once a day);
- Use a hot iron to iron underwear and sheets;
- Perform hygienic procedures in the anal area twice daily to prevent pinworms;
- Wear elastic-banded underwear at night;
- Perform a thorough wet cleaning of the premises.